The opposite color of brown is generally considered to be blue or bluish-grey. Brown is often categorized as a shade of orange, and since blue is the complementary color of orange, it is seen as the opposite of brown.
The complements of brown can vary depending on the specific shade, but in general, blue or bluish-grey is considered the opposite. This opens up a world of possibilities for creating captivating and harmonious color combinations, whether it’s in fashion, design, or any other creative endeavor.
By pairing brown with its opposite, you can create a visually striking and balanced look.
The Science Of Brown
Brown is a complex and versatile color that holds a unique place in the world of color theory. Understanding the science behind brown can provide valuable insight into its characteristics and how it interacts with other colors.
Breaking Down Brown
Brown is a mixture of different colors, often including shades of red, yellow, and blue. This combination results in a deep, earthy hue that is commonly associated with nature and stability. The presence of these underlying tones gives brown its distinct warmth and richness.
Brown On The Color Wheel
While brown may not appear on traditional color wheels, it is often considered a shade of orange or a dark variation of red. As a result, the opposite of brown falls within the blue color family. This relationship on the color wheel highlights the complementary nature of these colors, offering a range of possibilities for creating harmonious color schemes.
Credit: www.quora.com
Complementary Colors Explained
Understanding complementary colors is essential in creating visually appealing designs and artworks. Complementary colors are pairs of colors that, when combined, cancel each other out. This means that when mixed together, they create a neutral color. In the context of color theory, the opposite color of brown is crucial in creating balance and contrast in various visual compositions.
Color Theory Basics
Color theory is the study of how colors interact with each other. It involves the relationships between colors, their properties, and the visual effects produced by these interactions. The color wheel is a fundamental tool in understanding color theory, as it illustrates the relationships between primary, secondary, and tertiary colors, as well as complementary colors.
Finding Complementary Colors
Identifying the opposite color of brown can be achieved through referencing the color wheel. Brown is often considered a dark shade of orange, and therefore, its complementary color is located opposite it on the color wheel. In this case, the complementary color of brown is blue. This knowledge can be applied in various creative endeavors, such as interior design, fashion, graphic design, and painting, to achieve visually striking and harmonious results.
Brown’s Color Wheel Mystery
Dive into the intriguing world of color theory with ‘Brown’s Color Wheel Mystery’. Discover that the opposite color of brown typically falls within the blue family, offering a unique and harmonious contrast. Unveil the captivating relationship between these complementary hues.
Why Brown Is Absent
Brown’s absence from the traditional color wheel has long been a topic of intrigue and curiosity. While the color wheel typically consists of primary, secondary, and tertiary colors, brown is noticeably absent. This omission has sparked numerous discussions among artists, designers, and color enthusiasts alike.
Contemporary Interpretations
In contemporary interpretations of the color wheel, brown is often represented as a dark shade of orange. This placement is based on the understanding that brown is a more desaturated version of orange. Therefore, the opposite of brown is considered to be within the blue family. This means that shades ranging from light blue to deep teal or cyan can be seen as the opposite of brown.
Understanding brown’s opposite color can be beneficial in various creative endeavors. Whether you’re designing a color palette, creating art, or planning an interior decor scheme, knowing the opposite color of brown opens up a world of possibilities for creating captivating and harmonious combinations.
By recognizing that blue is the complementary color of brown, you can experiment with different shades and tones to achieve a balanced and visually appealing result. From subtle contrasts to bold juxtapositions, the interplay between brown and its opposite on the color wheel can add depth, vibrancy, and intrigue to any design.

Credit: blog.daisie.com
Blue: The Antithesis Of Brown
Brown and blue are opposite colors on the color wheel. While brown is a neutral earth tone that pairs well with other neutrals and brighter statement colors, blue is a cool-toned color that provides a calming effect and is often associated with water and sky.
Blue: The Antithesis of Brown
When it comes to color theory, opposites attract. In the world of colors, blue stands as the antithesis of brown. These two hues couldn’t be more different from each other, creating a striking contrast that captivates the eye. Let’s explore why blue is considered the complementary color to brown and how different shades of blue oppose the warm tones of brown.
H3: Blue as the Complementary Color
In the realm of color theory, complementary colors are pairs that create maximum contrast and enhance each other’s intensity. Blue and brown, despite their stark differences, create a dynamic complementary duo. Blue, with its cool and calming nature, acts as the perfect counterbalance to the warm and earthy tones of brown. This contrast creates visual interest and adds depth to any color palette.
H3: Shades of Blue Opposing Brown
Blue encompasses a vast spectrum of shades, each with its own unique characteristics. When it comes to opposing brown, different shades of blue come into play. Lighter shades of blue, such as baby blue or sky blue, provide a sharp contrast to darker shades of brown, creating a visually striking combination. On the other hand, deeper shades of blue, like navy blue or royal blue, offer a rich and intense opposition to lighter shades of brown.
To illustrate the contrasting nature of blue and brown, let’s take a closer look at their positioning on the color wheel. Brown, often considered a darker, desaturated version of orange, finds its opposite in the realm of blue. Depending on the specific shade, brown’s opposite can range from a light blue to a deep teal or cyan. This positioning on the color wheel solidifies the notion that blue is indeed the antithesis of brown.
In conclusion, blue stands as the complementary color to brown, offering a striking contrast that adds depth and visual interest to any color palette. Whether it’s the lighter shades creating a sharp contrast or the deeper shades providing a rich opposition, blue and brown create a captivating combination. Understanding the relationship between these two colors opens up a world of possibilities for creating harmonious and captivating designs.
Beyond Blue: Alternative Opposites
Discover the alternative opposites of brown with Beyond Blue. Explore the world of colors that complement and balance brown, from neutrals and earth tones to brighter statement colors. Unleash your creativity with the perfect color combinations for a stylish and harmonious look.
When Brown Leans Yellow
When we think of the opposite color of brown, blue is typically the first color that comes to mind. However, there are alternative opposites that can create unique and unexpected color combinations. One such alternative is yellow. When brown leans towards yellow, the opposite color shifts towards a bluish-purple. This creates a bold and vibrant contrast that can be used in various design and fashion applications.
Exploring Purple And Reddish Opposites
Another alternative opposite for brown is purple. Depending on the specific shade of brown, purple can create a striking and complementary contrast. For example, a light brown can be paired with a deep violet or plum, while a dark brown can be paired with a lavender or lilac. Additionally, reddish hues such as maroon or burgundy can also serve as an opposite to brown. These warm and rich colors can create a cozy and inviting atmosphere when paired with a neutral brown.
In conclusion, while blue may be the traditional opposite of brown, exploring alternative opposites such as yellow, purple, and reddish hues can offer unique and unexpected color combinations. Whether you’re designing a new logo or putting together an outfit, don’t be afraid to experiment with different colors and see what works best for you.
Color Correction In Practice
Using Opposite Hues
Brown’s opposite can range from light blue to deep teal or cyan. Brown is a desaturated version of orange, and blue is its opposite.
Correcting Brown Spots With Complementary Colors
- Orange cancels blue, ideal for under eyes and bruised skin.
- Pink cancels brown, perfect for camouflaging brown spots, age spots, and acne scarring.
- Complementary colors like blue can balance out brown tones effectively.
Design Applications
Brown, being a neutral color, pairs well with other neutrals and earth tones like black, cream, white, and olive green. It also works to balance out brighter statement colors. Additionally, the opposite of brown generally falls within the blue family, ranging from light blue to deep teal or cyan.
Interior Design
Brown’s opposite color is generally in the blue family.
Fashion And Beauty
Blue shades are commonly used to complement brown outfits.
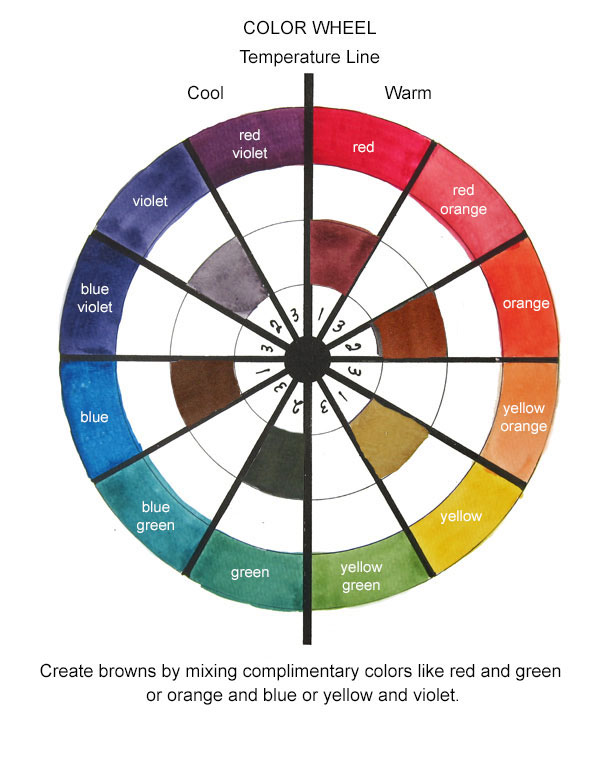
Credit: louisejacksonpaintingclasses.com
Creating Harmonious Palettes
When it comes to creating harmonious color palettes, understanding the opposite color of brown is essential for achieving balance and visual appeal in your designs.
Balancing Brown And Blue
Brown, a neutral color, pairs exceptionally well with various colors, but its opposite on the color wheel is blue. The dynamic contrast between brown and blue creates a visually striking and harmonious combination.
Innovative Color Combinations
By incorporating brown and blue into your palette, you can experiment with innovative color combinations that evoke a sense of sophistication and warmth. Consider adding accents of gold or cream to enhance the richness of these hues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Color Goes Well With Brown?
Brown pairs well with other neutrals and earth tones, such as black, cream, white, and olive green. It also balances out brighter statement colors.
What Color Cancels Brown?
Orange is the color that cancels out brown. It helps camouflage brown spots and is especially helpful for fair skin tones.
What Is The Negative Of Brown?
The opposite of brown is not a specific color, as it is considered a neutral color. However, on the color wheel, brown is often shown as a darker shade of orange and its opposite is generally in the blue family, ranging from light blue to deep teal or cyan.
Where Does Brown Fall On A Color Wheel?
Brown falls on a color wheel as a shade of orange. Its opposite color is generally considered to be in the blue family.
Conclusion
Understanding the opposite color of brown opens up a world of creative possibilities. Whether it’s blue, teal, or cyan, knowing the complementary colors for brown can help in creating harmonious designs and captivating visuals. Exploring this color theory can add depth and interest to various artistic endeavors.


